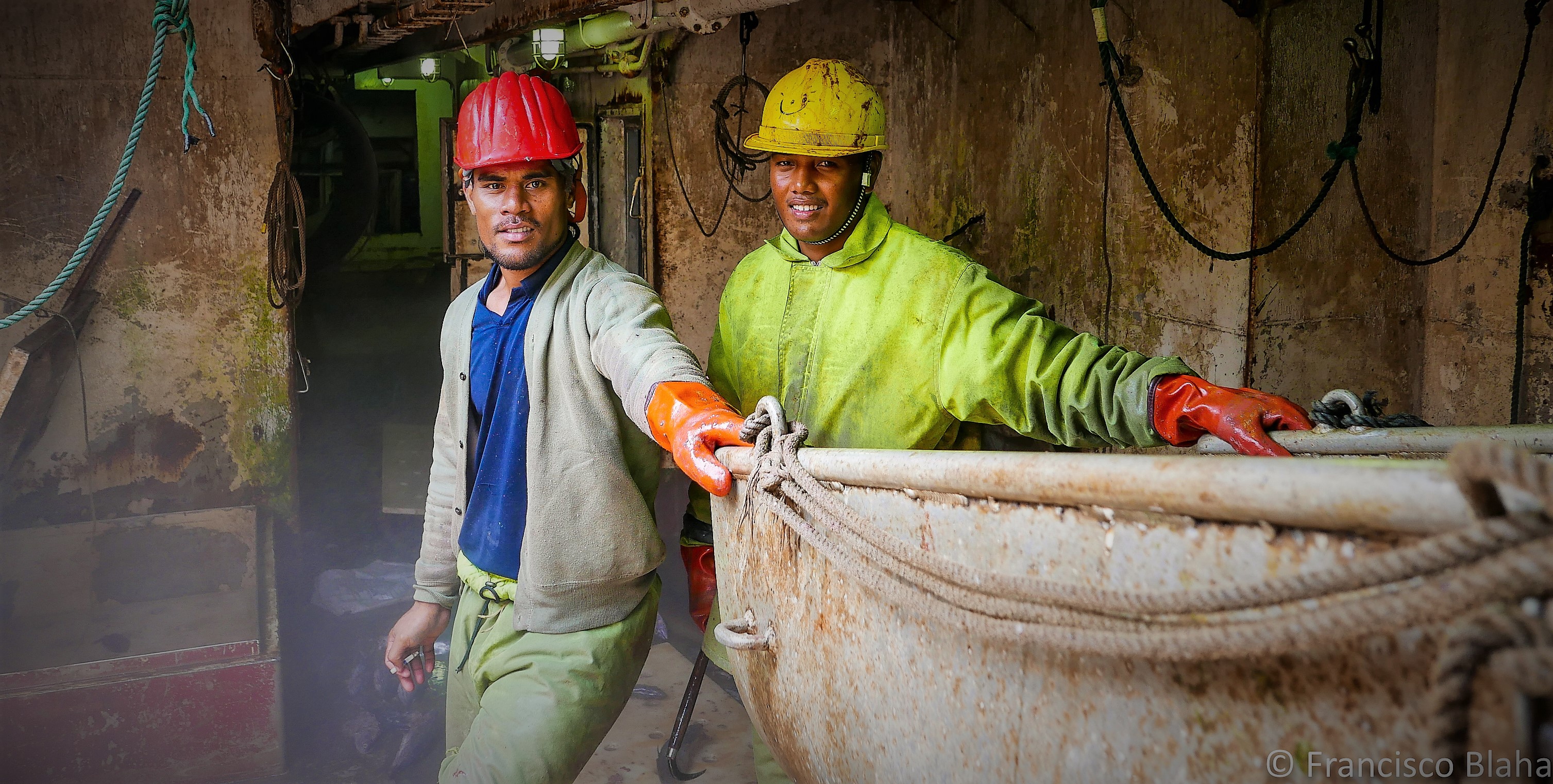
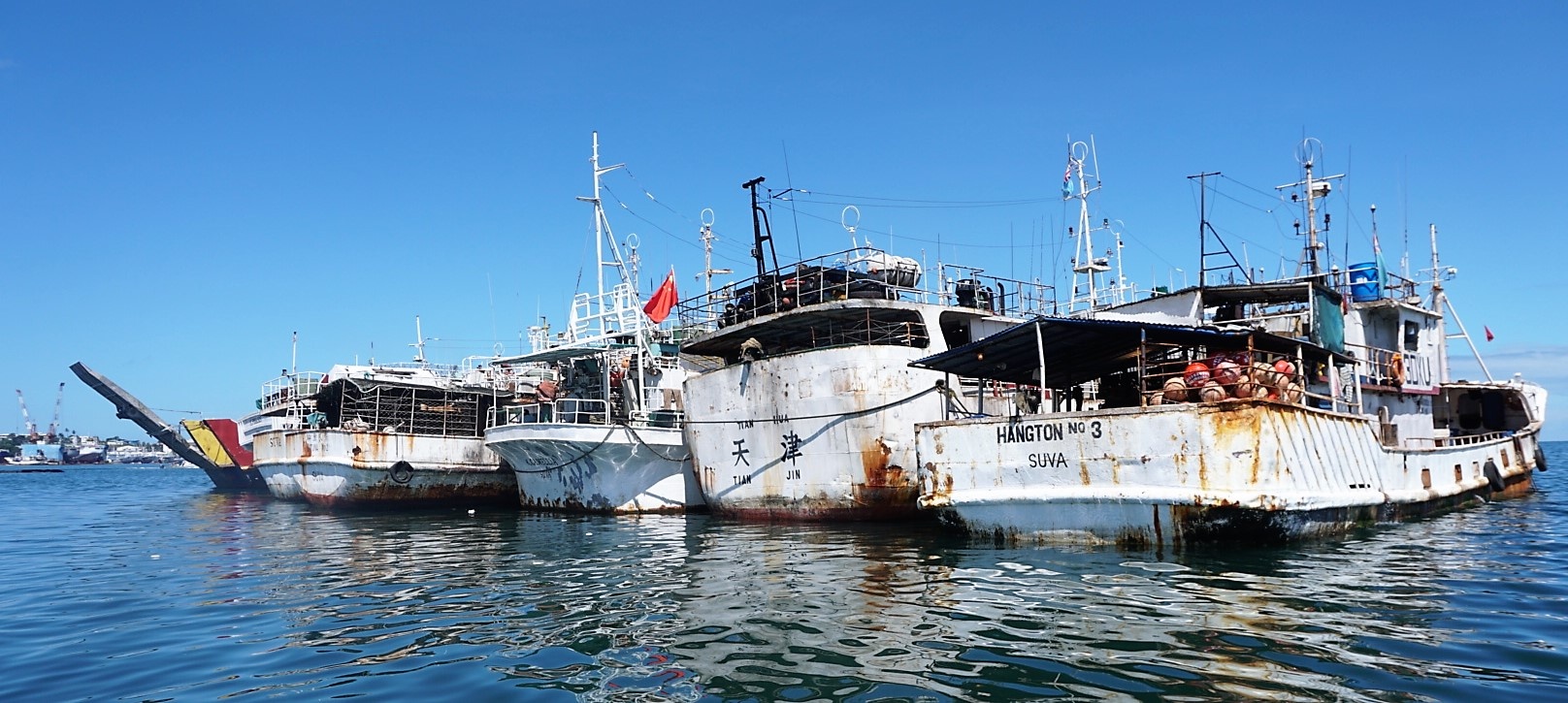
The international awareness of inequitable and often inhumane working conditions in the offshore fishing industry has increased in recent years.
Unfortunately, it has reached a point where offshore fishing is an industry that has become synonymous with poor working conditions and human rights abuses when compared with other ocean industries like shipping. This is because the activity of fishing itself takes place outside of the legal jurisdiction of any nation State, on the “high seas” and within EEZs where no State has sovereignty to make and enforce laws. In effect it is an industry where bad players can get away with being unregulated and through the regime of flag State registration effectively claim "immunity" from legal oversight in relation to working conditions. This is not to say all offshore fishing vessel operators are bad players but those fishing vessel operators who do want to comply with good employment standards do not compete on a "level playing field".
The awareness raised by civil society organisations (CSOs) and stakeholders has led to various recent developments, including the development of a specific International Labour Organisation Convention (“ILO”) (Work in Fishing Convention, 2007 (No. 188)) (“C-188”). C-188 entered into force in November 2017.
Six months ago, in Cape Town, South Africa, the provisions of C-188 were brought to bear by South African authorities against a foreign owned fishing vessel (a link to ILO’s report on this story can be found here).
The problem of unregulated labour standards in offshore fishing exists because some flag States who do have the legal jurisdiction to enforce labour standards on vessels on the high seas that are registered to that flag State lack the ability or willingness to regulate offshore fishing vessels that "fly their flag". Effective and universal flag State regulation is an issue of oceans governance and this is same issue that underpins Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (“IUU”) fishing on the high seas and within coastal States’ EEZs. Solving this ocean governance issue in the fishing industry would likely lead to direct benefits for Pacific Island States both because employment opportunities would improve for Pacific Islanders and because those fishing vessels that are well regulated are more likely to comply with conservation and management measures put in place to protect the Pacific’s essential fish stocks.
In this extended legal bulletin we summarise the international law problem of unregulated labour standards in the offshore fishing industry and consider recent efforts that provide steps in the right direction to bring an end to a shameful problem that should no longer be tolerated in the 21st century. After all, as things stand, on the high seas (areas beyond national jurisdiction) the transportation of slaves by sea is an international crime and is regulated by the law of the sea framework. Contrast this with forced/slave labour and human rights abuses on people “employed” on fishing vessels in the same areas of ocean, and who fall outside any effective regulatory law of the sea framework and as a consequence find themselves outside the reach and protection of the law. To change this may require an overdue shift in general international consensus to amend the current law of the sea and governance framework.